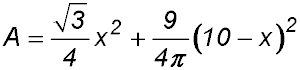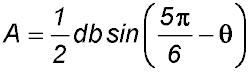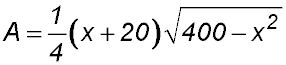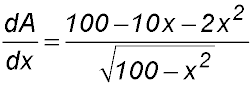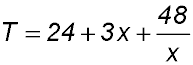Where the techniques of Maths
are explained in simple terms.
Calculus - Differentiation - Applied max/min questions.
Type 2: 2D shapes - Test Yourself 1.
- Algebra & Number
- Calculus
- Financial Maths
- Functions & Quadratics
- Geometry
- Measurement
- Networks & Graphs
- Probability & Statistics
- Trigonometry
- Maths & beyond
- Index
| The questions on this page focus on situations: |
| 1. creating two shapes. |
| 2. addressing areas including paddocks, etc |
| 3. involving geometric shapes. |
| 4. measuring the distance between two curves. |
| Creating 2 shapes. | 1. A wire of length 30 cm is cut into two pieces. One piece is then bent to form an equilateral triangle with each side of length x cm. The other side is bent to form a circle.
Answer.Length is 18.69 cm. |
| Areas and paddocks. | 2. A farmer has a straight river running through her property. She wishes to create a small field using the river as one side.
If the farmer has 200 metres of fencing, what dimensions must she make the field so as to enclose the largest possible area? Answer.Dimensions are 50 m × 100 m. |
| 3. The diagram shows the graph of y = (x - a)2.
The point P (p, (p - a)2) lies on the curve (with 0 < p < a). The tangent at P is drawn to intersect with the x and y axes at points A and B respectively. Answer.(ii) P is (a/3, 4a2/9). |
|
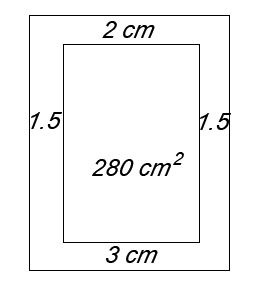
| 4. A printed page of a book is to have side margins of 1.5 cm, a top margin of 2 cm and a bottom margin of 3 cm.
The printed area of the page is to be 280 cm2 in area.
Find the dimensions of the page (to 1 dp) if the area of the paper used is to be a minimum. Answer.Page size is 16.0 × 21.6 cm. |
|
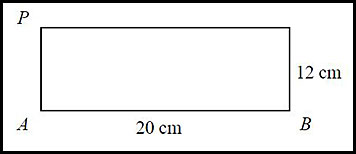
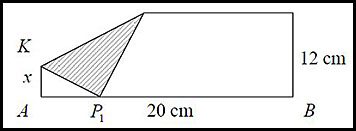
| 5. A rectangular paper has dimensions 12 cm wide and 20 cm long as shown.
The corner at P is then folded down and placed on point P1.
When this fold is made, a small triangle △KAP1 is formed at the bottom left. Let KA = x cm.
|
|
6. 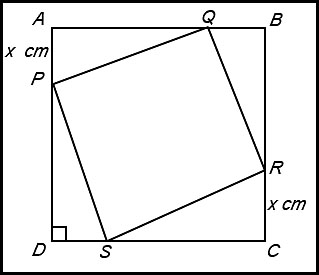
ABCD is a square of side 10 cm. PQRS is another square with vertices on the four sides of ABCD. It is known that BQ = CR = DS = AP = x cm. Answer.For a minimum, x = 5 cm. |
|
| Geometric shapes. | 7. |
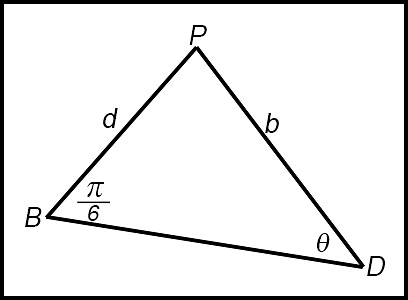
| 8. The triangle PDB with fixed side lengths b and d is shown below.
|
|
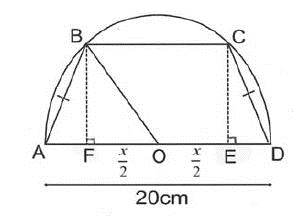
| 9. ABCD is a trapezium inscribed in a semi-circle of diameter 20 cm as shown.
AB=CD and O is the centre of the semicircle.
Answer.For max area, BC = x = 10 cm. |
|
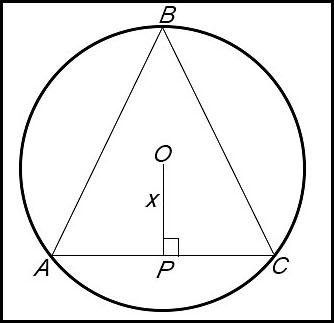
| 10. An isosceles triangle ABC is inscribed in a circle of radius 10 cm. OP = x and OP bisects AC such that AC is perpendicular to OP. Copy or trace the diagram.
|
|
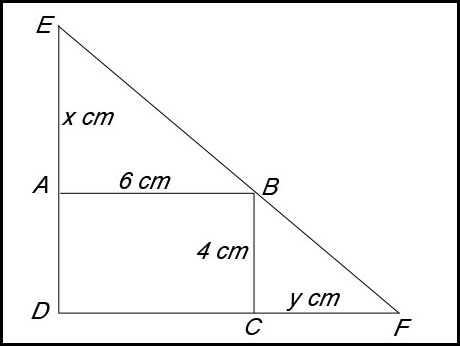
11. In the diagram above, ABCD is a rectangle with AB = 6 cm and BC = 4 cm. E and F lie on the lines DA and DC respectively so that E, B and F are collinear. Let AE = x cm and CF = y cm. Answer.For min area, height, h = 8 cm and base = 12 cm. |
|
| Distance between 2 curves. | 12. A is on the curve y = (x – 2)2 + 9 and B is on the curve y = x (6 – x).
Answer.Min length of AB = 0.5 units. |
| 13. |